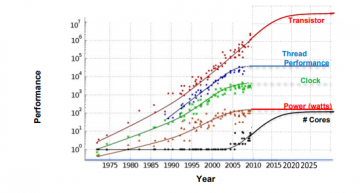
Over the past four decades, performance and energy efficiency in scientific computing technologies improved rapidly to produce lightning-speed computations but are expected to taper off as systems develop characteristics of extreme heterogeneity. Original figure courtesy of Kunle Olukotun, Lance Hammond, Herb Sutter, and Burton Smith. Figure extrapolations extended in 2016 by J. Shalf.
Exponential growth in classical computing over the last two decades has produced hardware and software that support lightning-fast processing speeds, but advancements are topping out as computing architectures reach their power and performance limits. Over time, computer architectures have become much more complex.